In daily life, we use wallets to store money, while in the context of virtual assets, "wallets" are used to store and send/receive virtual assets.
Understanding public keys and private keys
To understand how virtual asset wallets work, we must first understand the concept of public key and private keys. Virtual asset wallets use private and public keys to protect and gain access to virtual assets. The public key is the address of the virtual asset on the blockchain, similar to a bank account number, it can be publicly displayed to others for receiving virtual assets. On the other hand, the private key is the password that proves ownership of the virtual assets, and the holder of the private key can transfer their virtual assets to another address. A private key can generate the public key through algorithms, but the public key cannot be used in reverse to generate the private key. This helps ensure the security of the private key and, consequently, the virtual assets. Virtual assets are built on decentralized systems where a central authority is absent to keep a record of virtual asset ownership. Once the private key is lost or stolen, users may no longer be able to access or use their virtual assets. As such, users should always keep the private key safe with backup.
Since private keys are long and complicated, some virtual asset wallets generate a set of "mnemonic" which is usually composed of 12 to 24 English phrases making it easier to record and remember. In fact, mnemonic is another form of private key and must be kept securely. Users should try to save it in a handwritten format and store it in a safe place, and avoid storing it in the form of screenshots or photos.
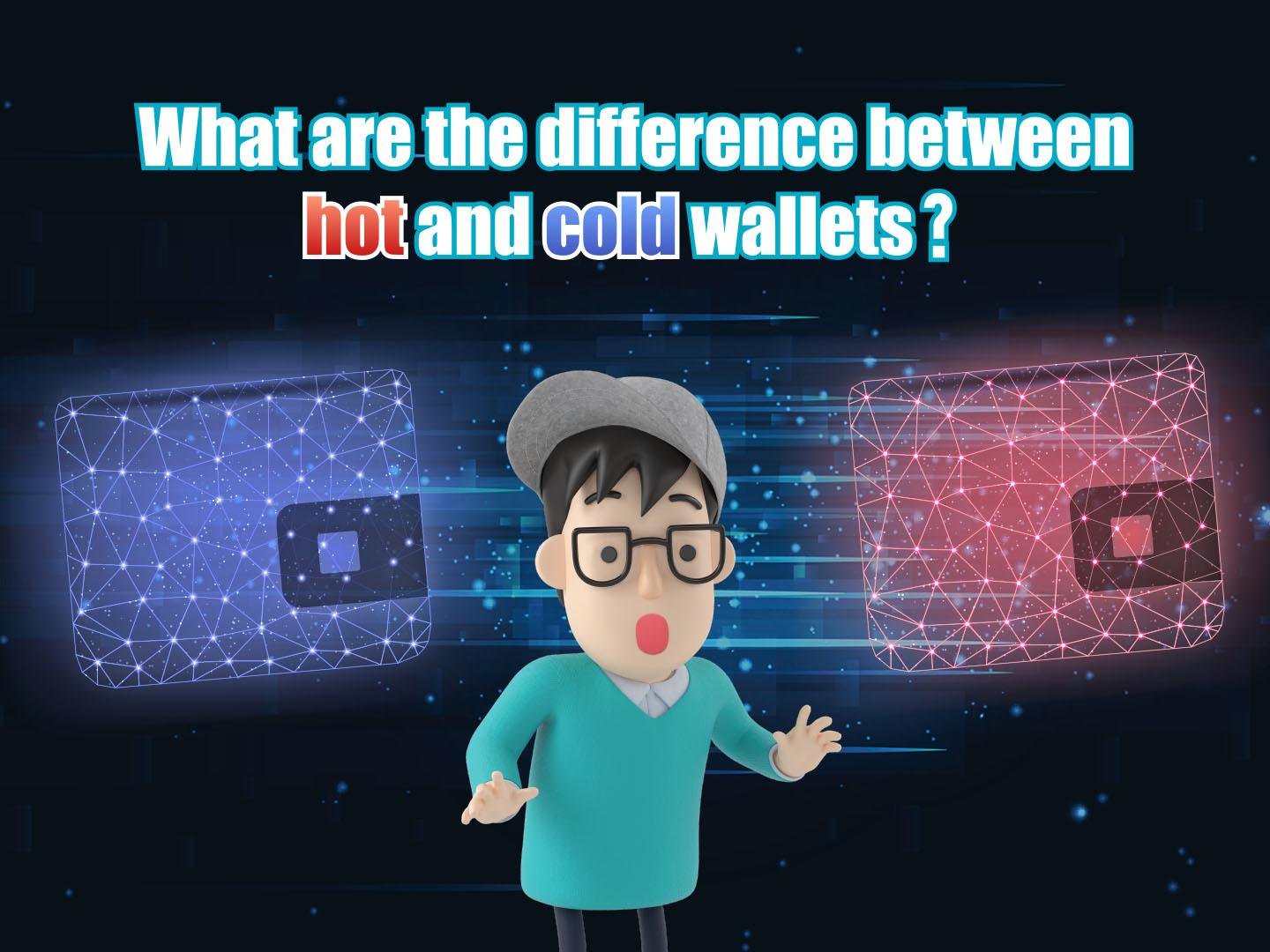
Public keys and private keys are stored in virtual asset wallets protected by a set of passwords. Virtual asset wallets can be broadly classified as cold wallets and hot wallets.
Cold wallets
Cold wallets refer to hardware devices that are not connected to the network, and most of them look like USB hard drives, car remote keys or credit cards. They store the private keys offline, offering better protection for virtual assets.
Hot wallets
A hot wallet refers to the storage method of virtual assets connected to the network. The advantage is that users do not need to purchase additional devices, and they can skip the steps of connecting to the network for each transaction like cold wallets. It is more convenient to send and receive virtual assets. However, any programmes/devices that connect to the internet share the same risk, that is, once the computer or mobile phone is invaded by viruses or malware, the private keys inside may be stolen. There are two types of common hot wallets:
- Software wallets
A software wallet is a software application. After downloading and installing it on a computer or mobile device, the private key can be generated.
- Trading platform-based wallets
Trading platform-based wallets are storage services provided by virtual asset trading platforms. The difference between these wallets and software hot wallets is that the trading platforms hold and manage private keys on behalf of the clients, allowing users to quickly deposit and withdraw their virtual assets. Since users of the trading platform-based wallets do not have control over the private key, they may lose their virtual assets if the trading platform is hacked, collapses or ceases operation, especially most trading platforms are currently unregulated and may be located overseas.
Not your keys, not your coins
Investors can choose a suitable virtual asset wallet according to their needs. Since hot wallets are not as secure as cold wallets, users should try to avoid storing large amount of virtual assets in hot wallets to reduce risks. In addition, investors should note that if virtual assets are stored on a trading platform, they may lose all their virtual assets if the platform collapses or ceases operation or is hacked.
No matter which types of wallets you choose, the first step in managing virtual asset wallets is to safely store the private key to reduce the risks. As mentioned above, the private key is the proof of ownership of virtual assets, and once it is lost, it means losing the virtual assets that the key protects. Therefore, make sure you keep the wallets and private keys safe, back up the private keys offline and store them in a safe place.